Lets assume an infinitely repeated prisoner’s dilemma game by two players. The resulting payoffs at each phase by the actions of two players are illustrated below in the table (payoffs are symbolized like (payoff for player 1, payoff for player 2)). Two players find out their strategies simultaneously and independently to maximize the expected payoffs of their own based on their information. The game is potentially infinitely repeated, though the game ends at a probability of 1–x (0≤1–x≤1) in every phase (that is, such players continue to play this game at the probability of x). There is no discount rate for the future payoffs (that is, both players weight current and future payoffs equally).
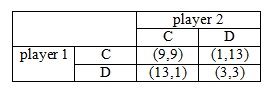
(a) Assume two players adopt a Trigger Strategy (Play C in the first phase In the tth phase(t≥2), if the outcome of all t–1 preceding stages has been (9, 9), then play C; or else play D). Find the range of x which makes cooperation self-sustainable.
(b) Assume two players adopt a Tit for Tat Strategy (TFT) (Play C in the first phase And then, do whatever the other player did at the previous phase). Find the range of x which makes cooperation self-sustainable.