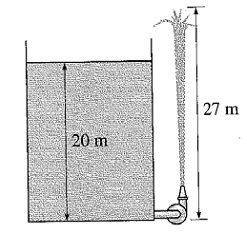
The water level in a tank is about 20 m above the ground. A hose is joined to the bottom of the tank, and the nozzle in the end of the hose is pointed to straight up. The tank is at sea level, and the water surface is open to the environment. In the line leading from the tank to the nozzle is a pump, that rises the pressure of water. If the water jet increases to a height of 27 m from the ground, then find out the minimum pressure rise that is supplied by the pump to the water line.