The shells of marine organisms contain calcium carbonate CaCO3, largely in a crystalline form known as calcite. There is a second crystalline form of calcium carbonate known as aragonite. Physical and thermodynamic properties of calcite and aragonite at 298 K and 1.0 bar are given in the following table.
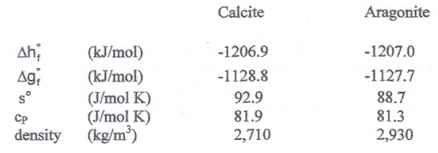
i) Would you expect an isolated sample of calcite at 298 K and 1.0 bar to convert to aragonite via the reaction (or phase transition)
CaCO3calcite → CaCO3aragonite
given sufficient time? Explain.
ii) Determine the minimum pressure that must be exerted on calcite at 298 K to form aragonite. Assume that calcite and aragonite form pure solid phases that are incompressible and insoluble in each other.
iii) Can calcite be converted to aragonite at P = 1.0 bar if the temperature is increased? Explain.