Below is a drawing of the wall of a refrigarator which consists of 3 layers- 0.2 cm thick steel walls on both sides of 4 cm of glass wool. This refrigarator was initially turned off so the temperature inside and out side was the same and the flux of heat through the wall was zero. Assume the refrigarator were turned on, the temperature inside was suddenly reduced to 4oC and answer the following questions.
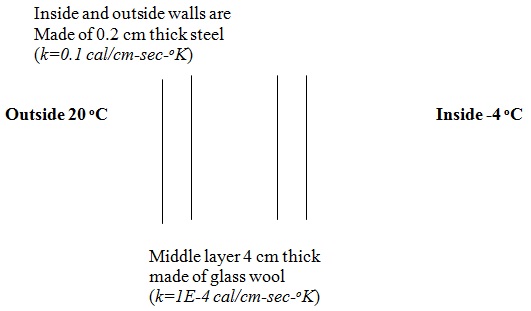
a) When would the heat flux through inside wall of the refrigerator be the greatest, immediately after the inside temperature was reduced or after the heat flux through the wall reach steady state? Explain.
b) When would the heat flux through the outside wall of the refrigerator be the greatest, immediately after the inside temperature was reduced or after the heat flux through the wall reach steady state? Explain.
c) Calculate the steady state heat flux through the wall assuming the outside temperature is 20 oC.
d) Could you use either the Reynolds or Chilton-Colburn analogies to get a mass transfer coefficient appropriate for this system? Explain.