Solve the system Ax = b, with
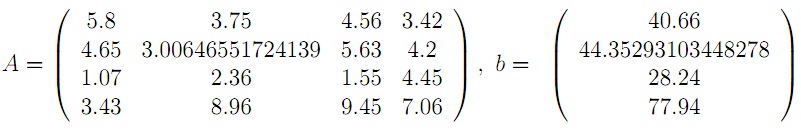
using the given Matlab function gauss (it calls backsb which is also provided) that performsGaussian elimination without pivoting. Then use the built-in Matlab function (x = Anb), which uses Gaussian elimination with partial pivoting. The correct solution to the above system is xT = [1; 2; 3; 4]. Comment on the accuracy of the solution obtained by both algorithms. Your comments should have a theoretical basis, they should also refer to your computational results when needed.