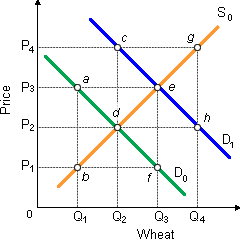
Suppose the U.S. wheat market is primarily in a stable equilibrium upon S0D0. Assume now that the government institutes a legal price floor at P3 per bushel of wheat. When the government will buy and store any resulting surplus, thus keeping a quantity of wheat off the market, in that case: (1) taxpayers will make total payments to farmers equivalent to 0Q1aeQ3 for unconsumed wheat. (2) Americans as eventual wheat consumers will buy Q1 wheat at price P3. (3) total revenue annually for farmers will equivalent 0P3eQ3. (4) the gains to farmers will be exceeded through losses to taxpayers and consumers, therefore this agricultural policy causes economic inefficiency. (5) all of the above.
Can anybody suggest me the proper explanation for given problem regarding Economics generally?