When this profit-maximizing firm as in illustrated graph can’t price discriminate in that case this will operate where is: (1) accounting profit is positive but economic profit is zero. (2) the demand curve facing the firm is the least price elastic. (3) total revenue equals the sum of marginal fixed costs. (4) marginal revenue most greatly exceeds average revenue. (5) marginal costs equal variable costs.
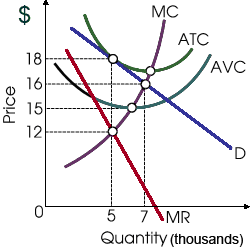
Hello guys I want your advice. Please recommend some views for above Economics problems.