NUCLEAR PHYSICS (PHY555) HOMEWORK #1
1. Calculate the luminosity for a beam of protons of 1 µA colliding with a stationary liquid hydrogen target 30 cm long. Compare this to a typical colliding beam luminosity of ∼1034 cm-2s-1.
2. An imaginary accelerator consists of colliding beams of electrons and protons, each of 2 TeV total energy. What laboratory energy would be required to achieve the same center-of-mass energy if electrons collide with stationary protons? Repeat the calculation for beams of 2 GeV instead of 2 TeV.
3. Beams of electrons and protons, both traveling at almost the speed of light, collide. The electrons and protons are in bunches 2 cm in length in two rings of 300 m circumference, each of which contains one bunch. Each bunch contains 3x1011 particles, and the circulating frequency is 106=sec for each beam, so that 106 bunches collide with each other per second. Assume that the particle is distributed uniformly over cross-sectional areas of 0.2 mm2, and that this is also the area of the intersecting collision region.
a) Determine the luminosity
b) If the cross section for collisions is 10 µb, determine the number of scattering events per second that would be observed in a counter totally surrounding the intersection region.
c) Find the average x of electrons.
d) If the beam of electrons scatters from a stationary target of liquid hydrogen (density ≈ 0.1 g/cm3) 2 cm long, rather than with the circulating proton beam, find the number of scattering events and compare to part b).
4. The Rutherford scattering amplitude can be written as:
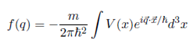
where V(x) is the scattering potential and q = p ?? p0 is the momentum transfer of the alpha particle (Z1e) to the target (Ze). Assume V(x) is the Coulomb potential of a nucleus shielded by an electron cloud. Use the form:
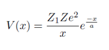
where a is a length of characteristic of atomic dimension. Using this amplitude, and the fact that the target charge distribution is spherically symmetric to derive the Rutherford scattering amplitude in the form:
f(q2) = -2mZ1Ze2/q2 +?/a)2
Finally, rewrite this equation in terms of the kinetic energy of the incident alpha particle and the scattering angle.
5. Assume a probability distribution given by (x=j x j)
(4) x <= R : ρ(x) = ρ0
(5) x > R : ρ(x) = 0
a) Compute the form factor for this uniform charge distribution.
b) Calculate < x2 >1/2
6. Download and read the paper, "New measurements of the protons's size and structure using polarized photons", by John Arrington. Answer the following questions with no more than a paragraph of written response for each question.
a) What are the two methods being used to extract the electric and magnetic form factors, GE and GM?
b) Qualitatively, how does the extracted ratio GE/GM differ for these two methods?
c) What is the current explanation for the difference in the ratios between these two types of measurements?