The number of molecular orbitals and molecular motions of each symmetry type can be deduced.
Let us continue to use the C2v point group and the H2O molecule to illustrate how the procedure developed in preceding sections can be used to deduce the symmetry of molecular properties.
Bond orbitals to molecular orbitals: suppose that the electrons in one bond of an H2O molecule are described by a bond Ø1 and those in the other bond by Ø2. These bond orbitals can be used to construct molecular orbitals. Each molecular orbital must transform according to one of the symmetry species of the C2v point group, that to which the H2O molecule belongs.
The transformation matrices that describe the effect of the various symmetry operations on the two bond orbitals can be seen.
The characters of the representation provided by these transformation matrices are the sums of the diagonal elements. If we write 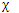 to represent the characters, we have
to represent the characters, we have

According to the deduction these are also the characters that would have been obtained if we had used molecular orbitals as a basis. But the characters for each molecular orbital must be drawn from those for the irreducible representation of the point group.
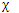 =
= 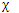 Ai +
Ai + 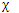 Bi
Bi
Thus we have discovered that the molecular orbitals, the eigenfunctions for the H2O molecule that are constructed from orbitals along the individual bonds, must be of the symmetry types A1 and B1.
A convenient way to obtain characters: the transformation matrices do not have to be written to obtain the characters 2, 0, 2, 0 shown above. A diagonal element occurs only if the bond is turned into itself or in other cases turned into the opposite of itself. Bonds (or vectors or orbitals) shifted from one to another equivalent atom do not degenerate any diagonal elements. Thus, with for each symmetry operation we write a contribution of +1 for each unshifted bond orbital. The result for E is 2, for C2 is 0, for σv is 2, and for σ'v is 0. These are the same characters as we obtained earlier by working out the transformation matrices.
Translations, rotations and vibrations: now let us see whether we can classify the overall translational and rotational motions and the vibrational motions of the H2O molecule according to symmetry. We begin as in the analysis of the number of degrees of freedom by treating these motions in terms of the three displacement coordinates on each atom. These 3n vectors provide a basis on which the symmetry operation of the C2v group, to which the H2O molecule belongs, can act.
We need not work out the 9 × 9 transformations matrices that describe the effect of E, C2, σvand σ'v on the nine displacement vectors. We need only deduce the characters i.e. the sum of the diagonal elements, of these matrices.
An entry occurs along the diagonal of a transformation matrix for an atom cannot exchange places with another atom as a result of the symmetry operation. Thus for each exchange places operations effect of each symmetry operation will be to leave each of these vectors unchanged or to reverse them. In the former case a + 1 will be contributed to the diagonal terms; in the latter case a - 1 will be contributed. Inspection of the effect of the symmetry operations on the nine displacement vectors that provide a basis for the translations, rotations, and vibrations of the molecule gives

Now, in principle, a change in coordinates could be found such that the nine displacement coordinates would combine to give coordinates for the three translational motions and the three rotational motions of the molecule as a whole and the three vibrational motions of the atoms of the molecule. (Such a transformation was worked through for diatomic molecules.
The transformation matrices that describe the effects of the symmetry operations on these new displacement sets would be different from those describing the effects on the displacement vectors. But the sum of the diagonal elements of these transformation matrices would be unaffected. Thus we can treat the set of numbers 9, -1, 3, 1 as being the net characters for the three translational, three rotational, and three vibrational motions.
We can express the result by writing
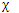 = 3
= 3 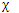 A1 +
A1 + 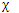 A2 + 3
A2 + 3 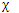 B1 + 2
B1 + 2 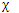 B2
B2