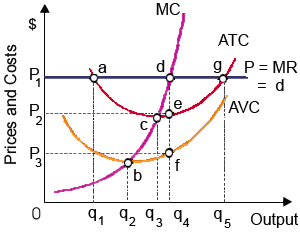
For this purely competitive firm, area P2P1de shows: (1) fixed cost (TFC). (2) losses, but the minimum possible economic loss. (3) average fixed cost (AFC). (4) maximum economic profits. (5) the rate of return on investment.
Can anybody suggest me the proper explanation for given problem regarding Economics generally?