When equilibrium moves from point a to point b, the simple market experiencing a raise in supply is demonstrated within: (w) Panel A. (x) Panel B. (y) Panel C. (z) Panel D.
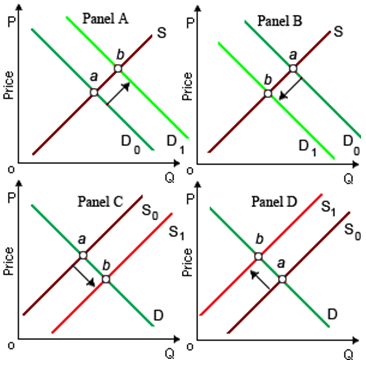
Hello guys I want your advice. Please recommend some views for above economics problems.