Problem:
Luke likes to consumer CDs (good1) and pizzas (good 2). His preference over both goods is given by the utility function
U(x1; x2) = x21 x42.
If Luke allocates $200 to spend on both goods and if a case of CDs costs $20 and a pizza costs $10, how many cases of CDs and pizzas would he consume in order to maximize his utility subject to his income. Show your work and illustrate your answer graphically.
Summary:
The problem in economics in price theory deals with deriving maximum marginal utility and marginal rate of substitution.
Answer:
U(x1, x2) = x12x24
P1 = 20, P2 = 10
MUx1 = 2x1x24
MUx2 = 4x12x23
Therefore, MRS = ½(x2/x1)
Now, for optimization, MRS = P1/P2 = 20/10 = 2
Now, ½(x2/x1) = 2
x2 = 4x1
Putting this value into the budget equation:
20x1 + 10x2 = 200
20x1 + 40x1 = 200
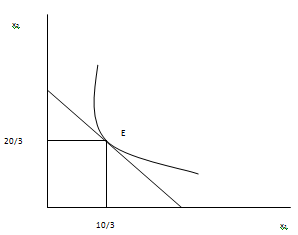
x1 = 10/3
and x2 = 40/3