When cranberries are a constant cost industry and that firm is typical, in that case the industry’s long-run supply curve is curve as: (i) curve A. (ii) curve B. (iii) curve C. (iv) curve D. (v) curve E.
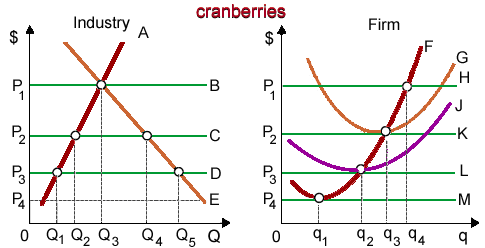
Please choose the right answer from above...I want your suggestion for the same.