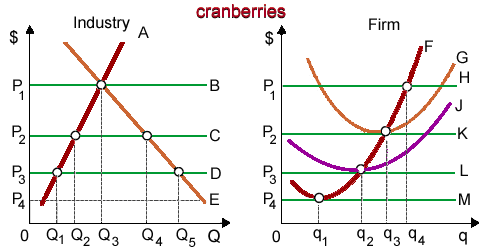
When the price for cranberries is primarily P1, in that case in the long run: (w) firms will neither enter nor exit this industry. (x) entry of firms will move curve supply curve A to the right. (y) exit of firms will move supply curve A to the left. (z) entry of new firms will shift this firm’s curve F to the right.
How can I solve my Economics problem? Please suggest me the correct answer.