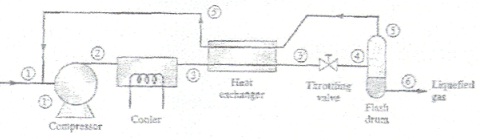
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is produced using a Linde liquefaction process from pure methane gas at 3 bar and 280 K (conditions at point 1 in figure below). A three-stage compressor with interceding is used to compress the methane to 100 bar (point 2). The first stage compresses the gas from 1 bar to 5 bar, the second stage from 5 bar to 25 bar, and the tiiird stage from 25 bar to 100 bar. Between stages the gas Is isobarically cooled to 280 K. Each stage of the compressor can be assumed to operate reversibly and adiabaticaliy. The methane leaving the cooler is at 100 bar and 210 K (point 3). The flash dram is adiabatic and operates at! bar. The recycled methane leaving the heat exchanger (point 5') is at I bar and 200 K.
a) Calculate the fractions of vapour and liquid leaving the flash drum {Hint: write balance equations around the subsystem consisting of the heat exchanger, throttle valve and flash drum).
b) Calculate the temperature at the inlet of the compressor (point I).
c) Calculate the amount of work required for each kilogram of methane that passes through the compressor.
d) Calculate the amount of compressor work required for each kilogram of LNG produced.
e) Calculate
i) the heat removal after the first and second stages of the compressor,
ii) the heat removed in the cooler, and
iii) the heat exchanged in the heat exchanger.
Express all values in kJ/kg of methane that passes through the compressor.
Data: The thermodynamic properties of methane are given in the attached diagram.