Laws of Chemical Combination- In order to understand the composition of the compounds, it is necessary to have a theory which accounts for both qualitative and quantitative observations during chemical changes. Observations of chemical reactions were most significant in the development of a satisfactory theory of the nature of matter. These observations of chemical reactions are summarized in certain statements known as laws of chemical combination. These are:
1-Law of conservation of mass
2-Law of constant composition
3-Law of multiple proportions
4-Law of reciprocal proportion
5-Law of combining volumes (Gay Lussac's law of gaseous volume)
1-Law of conservation of mass-This law deals with the masses of reactant & the products of any chemical reaction (or a physical change).It was studied by French chemist Antoine Lavoisier. This law may be stated as follow-In all the chemical & physical changes, the total mass of the reactants is equal to that of the products. . It is a derivation of Dalton's atomic theory 'atoms neither created nor destroyed'.
Total masses of [reactants=products+unreacted reactants]
For example-1-A piece of ice in flask (weighted) is heated gently to melt ice (solid) into water (liquid) & again weighted. It's found that there is no change in weight though a physical change has taken place.
2-If 5.2 g of CaCo2when heated produced 1.99 g of Carbon dioxide and the residue (CaO) left behind weighs 3.2g.
So the total weight of the products (CaO +CO2) = 3.20+ 1.99 = 5.19 g
Difference between the wt. of the reactant and the total wt. of the products= 5.20 - 5.19 =0.01 g.
This small difference may be due to experimental error. Thus law of conservation of mass holds good with in experimental errors.
2-Law of constant composition or the definite proportions-This law was given by J.L.Proust & deals with the composition of elements present in a given compound. It states that- A chemical compound always contains same elements combined together in same proportion by mass. and it does not depend on the source of compound. For example-CO2 can be obtained by different method such as
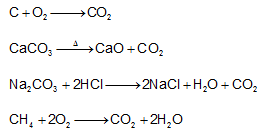
The composition of CO2 obtained by different means always having same C: O ratio =12/32 = 0.375 by mass.
Limitations of law of constant composition are-
(i)This law is not applicable if an element exists in different isotopes which may be involved in formation of compound.e.g.In the formation of CO2, if C-12 isotope & C-14 isotope combine than the C: O is 12:32 & 14:32 respectively.
(ii)The compounds formed may be different but the elements may combine in same ratio.
3-Law of multiple proportion: It was studied by Dalton, which defined as follow-
When two elements combine to form two or more than two different chemical compounds then the different masses of one element which combine with fixed mass of the other element bear a simple ratio to one another.
For example: Carbon forms two oxides in oxygen
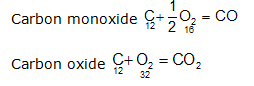
The ratio of masses of oxygen in CO and CO2 for fixed mass of carbon (12)
is 16 : 32 = 1: 2.
Similar with compounds of sulphur & oxygen-they also formed two oxides SO2 & SO3 so the ratio of masses of oxygen 32:48 or 2:3 respectively.
4-Law of reciprocal proportion: This law was given by Richter. It stated as follow-
If two elements combine separately with a fixed mass of a third element, then the ratio of their masses in which they do so is either same or multiple of the ratio in which they combine with each other. The above law is the basis of law of equivalent masses.
5-Law of combining volumes (Gay Lussac's law of gaseous volume) - It states that at a given temperature and pressure, when the gases combine they do so in volumes which bear a simple ratio to each other and also to the volume of gaseous product.
e.g. If one volume of hydrogen react with one volume of chlorine to form two volumes of hydrogen chloride gas. The ratio of volume of various reactant & product is 1:1:2 which is a simple whole number ratio. Similar in the formation of ammonia, the ratio of reactant nitrogen, hydrogen & ammonia is 1:3:2 which is a simple whole number ratio.