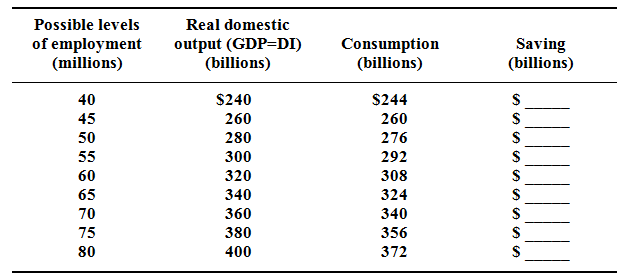
Utilizing the consumption and saving data in given table and supposing investment is $16 billion, describe saving and planned investment at the $380 billion level of domestic output? Determine saving & actual investment at that level? Determine saving and planned investment at the $300 billion level of domestic output? Describe levels of saving & actual investment? Employ the concept of unplanned investment to describe adjustments toward equilibrium through both the $380 and $300 billion levels of domestic output.