Individual demand and market demand schedules:
Individual demand schedule states the quantities required by an individual consumer at various prices.
Table: Individual demand schedule for oranges
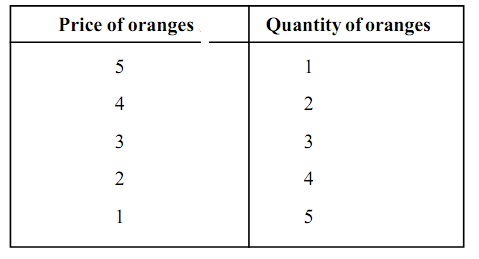
It is apparent from the schedule that whenever the price of orange is $ 5/- the consumer demands simply one orange. Whenever the price falls to $ 4 he demands for 2 oranges. Whenever the price falls further to $ 3, he demands for 3 oranges. Therefore, whenever the price of a commodity falls, the demand for that commodity rises and vice-versa.
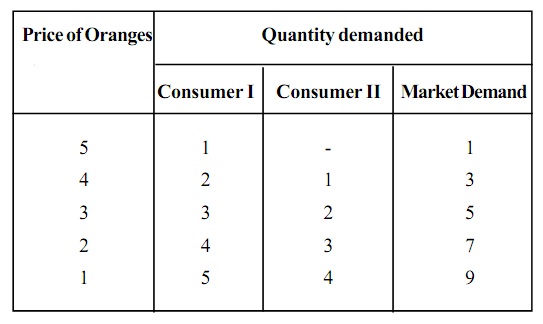
Market demand schedule:
A demand schedule for a market can be build by adding up demand schedules of the individual consumers in the market. Assume that the market for oranges comprises of 2 consumers. The market demand is computed as follows.
Table: Demand Schedule for two consumers and the Market Demand Schedule