The thermal part of the internal energy and the enthalpy of an ideal gas can be given a molecular level explanation.
All the earlier development of internal energy and enthalpy has been "thermodynamic". We have made no use of the molecular level understanding of energy that we obtained in the energy crisis. There you recall, we found that we could calculate the thermal energy contribution U- U0 for molecularity sample systems such as ideal gases. Now this thermal energy will be released to the thermodynamic internal energy and enthalpy.
The energy of a system when only the lowest available energy levels are occupied is derived on the concept of energy level. This is the energy that the system would have if the temperature were occupied. This is the energy were lowered to absolute zero and the system did not change its physical form. The thermal energy U- U0 is the additional process energy that the system would acquire if the temperature were raised from this hypothesis zero temperature form and the particles distributed thermodynamical energy themselves throughout the energy levels.
Thermal enthalpy H - H0: the general relation between enthalpy and internal energy is H - H0
For some liquids and solids at all ordinary pressures, the change in the PV term is small compared to changes in the H and U terms. As a result, at any temperature the enthalpy and internal energy are effectively equal. Thus H = u, H0 = U0, and H - H0 = U - U0. For standard state thermal enthalpies and internal energies we have
H0T - H00 + U0T - U00 [liquid or solid]
For gases, ideal behavior allows the PV term for a sample containing 1 mol of gas molecules to be equated to RT. When only the lowest energy states are compared, as occurs at the thermal energy results we can be converted to enthalpies by addition of RT. For standard state thermal enthalpies and internal energies we have various values for the thermal enthalpy at T = 298 K and for several other temperatures for some elements and compounds are included in this phenomenon.
Instance: nitrogen oxide, NO, forms from oxygen and nitrogen in internal combustion engines. (This reaction proceeds to a sufficient extent at the high temperatures of the engine for NO to be prodcue4d in amounts that cause serious pollution problems. Part of understanding the formation and decomposition of NO is based on the enthalpy change for the reaction at high temperatures, where NO is formed and at lower temperatures where it breaks up to N2 andO2.)
Calculate ΔH°0 and ΔH°2000 for the reaction in which NO is formed from its elements.
Answer: we begin by obtaining ΔH°0 as:
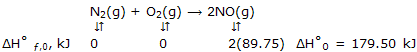
Now at any temperature, such as 2000K, which is representative of high temperatures at which calorimetric methods are not applicable, we have for N2, for example, H°2000 - H°0 = (H°2000 - H°298) + (H°298 - H°0) = 56.14 - (- 8.67) = 64.81 kJ. Then:
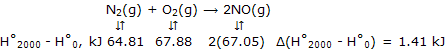
These values give:
ΔH°2000 = ΔH°0 + Δ(H°2000 - H°0)
= 179.50 + 1.41
=180.91 kJ
Notice that ΔH for the reaction can be deduced for any temperature at which the thermal energies of the reactants and the products can be calculated.