Transference numbers and molar conductors can be used to calculate ionic mobilities.
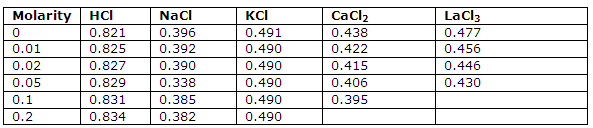
This tables under is giving the transference numbers for positive ions at 25 degree C and the values obtained by extrapolation to infinite dilution:
Molar ionic conductances and ionic mobilities at infinite dilution and 25 degree C.
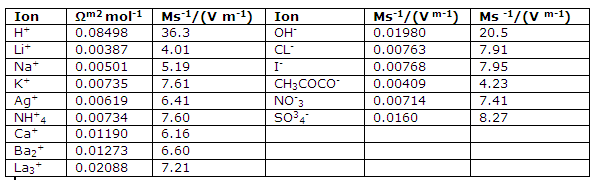
Values can now be obtained for the contributions the individual ions of an electrolyte make to the molar conductance. The empirical law of Kohlrausch implies that a infinite dilution the molar conductance can be interpreted in terms of such ionic contributions and that the contributions of an ion are independent of the other ion of the electrolyte. At infinite dilution, therefore, we wrote:
?° = v + λ°+ v- λ°- where
λ°+ and λ°- are the molar ionic conductors at infinite dilution. Since the transference numbers give the fraction of the total current by each ion, i.e., the fraction of the total conductance that each contributes, we can write;
v+ λ°+ = t°+ ?° and v- λ°- = t°- ?°
where t°+ and t°- are the transference numbers extrapolated to infinite dilution.
Ionic mobilities: consider a cell of the type used to introduce the concept of molar conductance. Such a cell consists of two electrodes 1m apart and of cross-section area A such that an amount of solution that contains 1 mol of electrolyte is held between the electrodes. For an applied voltage ∫, a current I will flow through the cell. These electrical quantities are related, since the conductance of such a cell is the molar conductance of the electrolyte, by:
I = ∫/R or I = ?∫
At infinite dilution the current can be attributed to the independent flow of positive and negative ions, and one can write:
I = ?°∫ = [v+ λ°+ + v- λ°- ] ∫ = v + λ°+ ∫ + v- λ°- ∫ = I+ + I-