Enzymes are complex proteinous substances, produced by living bodies, such as act as catalysis in the physiological reactions. The enzymes are, also called biochemical catalysts and the phenomenon is known as bio-chemical catalysis because numerous reactions that occur the bodies of animals and plants to maintain the life process are catalyzed by enzymes. Though enzymes are produced by living beings, they themselves are non-living and can act as catalysts even outside the living bodies. Enzymes are proteins with high molar mass ranging from 15000 to 1,000,000 g mol-1. Enzymes possess very high catalytic activity. They can increase rates of the reaction by 108 to 1020 times. The enzymes are extremely specific in nature. There is always a lock and key relationship between substrate (reactants) and enzymes. Due to this relationship between the substrate molecules can get attached to the enzyme molecule and then the reaction takes place. Enzymes are capable of bringing about complex reaction at body temperature.
Mechanism of enzyme activity
The stepwise mechanism of enzyme catalyzed reaction as proposed by Michaeli and Menten (1913) is being described as follows.
The reactant molecule attaches itself to the active site on the surface of enzyme. The active site in the given enzyme is so shaped that only a specific substrate can fit in it, just as a lock can be opened only with a specific key. The specific binding results in the creation of enzyme-substrate complex which is also referred to as activated complex.
In the complex, the substrate is located in the proper orientation to assist the chemical reaction and enhancing its rate. The complex finally decomposes to give products and regenerated enzymes. The general reaction system can be presented as:
Step I: binding of substrate (S) to enzyme
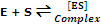
Step II: product formation of the complex
[ES]  [EP]
[EP]
Step III: release of the product from the enzyme
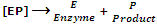
Characteristics of enzyme catalysis
The important characteristics of enzymes catalysts are:
High efficiency: enzyme catalysis increases the speed of reactions by 108 to 1020 times as compared to the uncatalysed reactions.
Extremely small quantities: extremely small quantities of enzyme catalysts - as small as millionth of a mole - can increase the rate of reaction by factors of 103 to 106.
Specificity: the enzyme catalysts are very much specific in nature. This means that one enzyme cannot catalyse more than one process. Almost every biochemical reaction is controlled by its own specific enzymes. For instance, the enzyme urease catalyses the hydrolysis of urea only and does not catalyse hydrolysis of any other amide. At the same time, none of the several thousand other enzymes present in the cell can catalyse hydrolysis of urea.
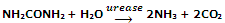
In the same manner, Maltase catalyses the hydrolysis of maltose and no other enzyme can catalyse its hydrolysis.
Optimum temperature and pH: the temperature at which enzyme activity is maximum is referred to as optimum temperature. The optimum temperature for enzyme activity is 37°C (310 K). The enzyme activity decreases on either side of optimum temperature. Similarly enzymes catalyzed reaction have maximum rate at pH around 7. Which is also called optimum pH value.
Enhancement of enzyme activity: Catalytic activity of enzymes is greatly enhanced by the presence of activators or co-enzymes. Activators are metal ions (Na+, Mn2+, CO2+, Cu2- etc) which get weakly bonded to enzyme molecules and therefore, promote their catalytic action. For example, the enzyme amylase shows high catalytic activity in the presence of NaCl which provides Na+ ions. Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds which are required by certain enzymes for their catalytic activity.