Problem 2
Consider Garfield's utility function given as
U(x1, x2) = x1x2,
where x1 is lasagna and x2 is "everything else". Suppose his allowance from Jon is
m = $8 and p1= $1 and p2= $1
(i) Find Garfield's optimal choice of lasagna and everything else and illustrate your answer graphically. Show your work.
(ii) Find an expression of Garfield's marginal rate of substitution between lasagna and all other goods and explain its meaning at the initial choice that you found in (i).
(iii) If the price of lasagna doubled, i.e., p1 increased from p1= $1 to p0= $2, what would be Garfield's new optimal bundle? Show the bundle on your graph.
(iv) Under the assumption that Garfield's demand for lasagna is linear, derive the demand equation from his two optimal bundles computed in (i) and (iii). Illustrate your answer graphically by drawing two graphs: one representing Garfield's optimal choice and the other representing his demand curve for lasagna driven from the two optimal bundles.
(v) Compute Garfield's price elasticity of demand for lasagna between the two prices p= $1and p0= $2 and explain its meaning.
(vi) Compute Garfield's price elasticity of demand at p1= $3:
(vii) If Garfield always consumes lasagna with garlic bread. Show the effect of an increase in the price of wheat on (a) the wheat market, (b) the bread market, and (c) the market for lasagna. Draw three graphs to illustrate your answer (one graph for each market). No calculations are necessary.
Summary:
This problem in price theory of economics deals with deriving maximum marginal utility, marginal rate of substitution and price elasticity of demand.
Answer:
(i) U(x1; x2) = x1x2;
M = 8, P1 = 1, P2 = 1
The MRS = MUx1/MUx2 = x2/x1
Now, MRS = P1/P2 = 1 => x2 = x1
Putting this in the budget constraint:
x1 + x2 = 8
2x1 = 8
x1 = 4
x2 = 4
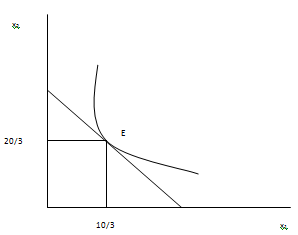
(ii)
Here MRS = 1.
This signifies that at the choice bundle of (4,4) Garfield will optimize his utility. Also, at this point the marginal utility from both the goods is equal. Therefore, he has no incentive to consumer more of one good while decreasing the consumption of other.
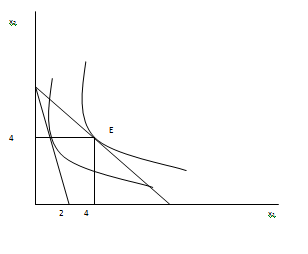
(iii) U(x1; x2) = x1x2;
M = 8, P1 = 2, P2 = 1
The MRS = MUx1/MUx2 = x2/x1
Now, MRS = P1/P2 = 2 => x2 = 2x1
Putting this in the budget constraint:
2x1 + x2 = 8
4x1 = 8
x1 = 2
x2 = 4
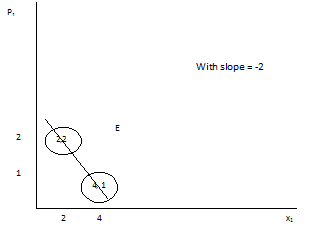
(v) % Change in quantity demanded = (2-4)/4 = -0.5
% Change in price = (2-1)/1 = 1
Therefore, elasticity = -0.5/1 = -0.5
Therefore, quantity demanded of lasagna will fall by 0.5%, if the price increases by 1%.
(vi) U(x1; x2) = x1x2;
M = 8, P1 = 3, P2 = 1
The MRS = MUx1/MUx2 = x2/x1
Now, MRS = P1/P2 = 3 => x2 = 3x1
Putting this in the budget constraint:
3x1 + x2 = 8
6x1 = 8
x1 = 4/3
x2 = 4
Now suppose price increases to 4.
U(x1; x2) = x1x2;
M = 8, P1 = 4, P2 = 1
The MRS = MUx1/MUx2 = x2/x1
Now, MRS = P1/P2 = 4 => x2 = 4x1
Putting this in the budget constraint:
4x1 + x2 = 8
8x1 = 8
x1 = 1
x2 = 4
Therefore, % change in price = 1/3 and % change in quantity = (-1/3)/ (4/3) = -1/4
Therefore, elasticity = (-1/4)/(1/3) = -3/4
(vii) (a)
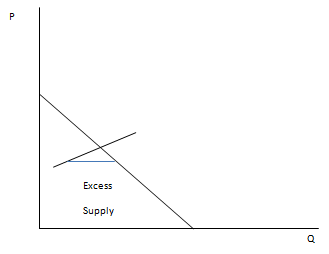
(b)
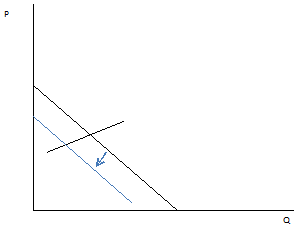
(c)