Question:
Explain why the free rider problem makes it difficult for perfectly competitive markets to provide the Pareto efficient level of a public good.
Answer:
A free rider is a person who cannot be excluded from the consumption or usage of a Public good, which is non-rivalrous and non-excludable in nature. The problem lies with the fact that these agents, the free riders, do not pay for the establishment and/or provision of the public good/property.
The free rider gains from this, as he/she gets all the gains from the good but does not have to pay anything for its provision.
Public goods have the special feature that if one person buys the good, everyone benefits from it. In this sense, the public goods have a positive externality attached to them. However, the free - rider issue leads to an undersupply of the public goods in a competitive market, as the perfectly competitive market does not take into account the externalities attached with a good.
The graph below illustrates it:
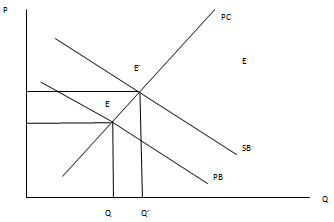
In the figure, PB denotes the personal benefit curve, SB denotes social benefits, and PC denotes personal cost. The optimal provision will be Q', taking into account the positive externality, however, the market equilibrium will be at Q, which does not take into account the positive externality of the public goods.