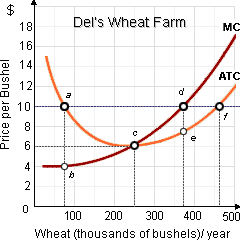
When the world price for wheat is $10 per bushel; and Del, who one owns the biggest wheat farm into North Dakota, will: (w) face a demand curve that is perfectly price elastic at $10 per bushel. (x) realize $4 per bushel in long-run economic profits. (y) operate at point c. (z) maximize profit by operating at point f.
Can someone explain/help me with best solution about problem of Economics...