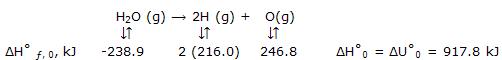Energy changes in some chemical reactions can be used to deduce the energies of chemical bonds.
Our understanding of the molecular basis of thermodynamic properties is extended when we ask why the enthalpy change for a reaction is what it is. We deduce, for example, from the data, the value of -802.34 kJ for ΔH°298 for the reaction:
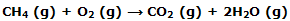
Why it is the enthalpy change has this value?
Two relatively small contributions to the ?H term can be recognized. One contribution comes from the difference in the normal products of the thermal energies of the molecules of the products and the reactants. Another small contribution due to the volume comes from the change in number of moles of reagents.
These minor complicating contributions can be avoided by using ?H00 = ?UC values such as those o f appendix table to calculate the ?U00 value of - 804.2 kJ for the methane combination reaction. Now we ask about the molecular basis of this energy difference.
To answer such question, we adopt a traditional chemical idea. We think of the energies of many substances in terms of the chemical bonds that we imagine to be holding the atoms together. The energy of one substance compared to that of another substance is said to be due primarily to the energy "strength" of the chemical bonds.
Standard enthalpies of atomic species: we need to justify the energy data for the free gaseous atoms to calculate the energy change when the molecules of a substance are broken up into free atoms.
Enthalpy and energy data can be taken for gaseous atomic substances. These data come, usually, from spectroscopic rather from calorimetric measurements. For diametric molecules, spectral studies show the energy for breakup of these molecules into atoms. Results from the original molecules and the atoms produced, all in their lowest energy, or ground states, can be deduced from the spectral data. Thus we arrive directly at data for ?H°f,0. these energy data for atomic species can be extended to give enthalpy values, as illustrated by some of the entries in bond energies.
Bond energies: with the data begin by considering reactions that are easily given a bond energy interpretation. For example, the ΔH° ƒ, 0 can be used to obtain: