The constant of vander Waal's equation can be related to the coefficients of the virial equation.
Vander Waal's equation provides a good overall description of the real gas PVT behaviour. Now let us focus on the description that this equation gives to the onset of nonideal behaviour. This stage is shown most clearly on displays of Z = PV/(RT) versus P. the first deviations from the ideal gas value of Z = 1 show up as straight line sections in Z-versus-P plots. These initial stages of non ideal behaviour are described by the simple virial expressions Z = 1 + BPP or Z = 1 + BV/V. we begin, therefore, by rearranging van der Waal's equation to a form that can be compared with the virial equations.
Multiplication of van der Waal's equation, in the form and for 1 mol by V/(RT) converts this equation to
PV/RT = V/(V - b) - a/RTV = 1/(1 - b/V) - a/RTV
We develop an equation with the form of the virial equation with volume terms by recognizing that the 1/(1 - b/V) term can be expanded by using the binomial expansion (1 - x)-1 = 1 + x + x2 + .... If only the first three terms of the series are exhibited, we develop to
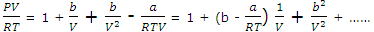
Comparison with virial equations, shows that van der Waals' equation implies the definition
BV = b - a/RT
Experimental values for BV for neon are plotted, notice that the temperature dependence of this second virial coefficient is generally consistent with that suggested values of BV are negative at low temperatures where the second term dominates, and these values increase and become positive at higher temperatures where the first term dominates. The curve is drawn on the basis with a and b values adjusted to give a good fit to the experimental results. Fitting second virial coefficient data provides, as this example illustrates, another way for assigning values to van der Waals' a and b parameters.
Van der Waals' excluded volume and molecular diameters
The excluded volume b, introduced by van der Waals' as an empirical correction term, can be related to the size of the gas molecules. To do so, we assume the excluded volume is the result pairwise coming together of molecules. This assumption is justified when b values are obtained from second virial coefficient data. Fitting values for the empirical constants of van der Waals' equation.
So that we need to deal with a single molecular size parameter, we treat molecules as spherical particles. The diameter of a molecule is d. the volume of a molecule is 4/3 ∏ (d/2)3.
The volume in which a pair of molecules cannot move because of each other's presence is indicated by the lightly shaded region. The radius of this excluded volume sphere is equal to the molecular diameter d. the volume excluded to the pair of molecules is 4/3∏d3. We thus obtain
Excluded volume per molecule = ½ (4/3 ∏d3)
= 4[4/3∏(d/2)3]
The expression in brackets is the volume of a molecule. Thus the excluded volume per molecule is 4 times the actual volume of the molecule.
Van der Waals' b term is the excluded volume per mole of molecules. Thus we have, with N representing Avogadro's number
B = 4 N [4/3∏ (d/2)3] = 4 N (volume of molecule)
Molecular size and Lennard-Jones Intermolecular attraction term based on second virial coefficient data:
| Gas |
Excluded volume b, L mol-1 |
Molecular diam. D, pm |
εLJ, J × 10-21 |
| He |
0.021 |
255 |
0.14 |
| Ne |
0.026 |
274 |
0.49 |
| Ar |
0.050 |
341 |
1.68 |
| Kr |
0.058 |
358 |
2.49 |
| Xe |
0.084 |
405 |
3.11 |
| H2 |
0.031 |
291 |
0.52 |
| N2 |
0.061 |
364 |
1.28 |
| O2 |
0.058 |
358 |
1.59 |
| CH4 |
0.069 |
380 |
1.96 |
| C(CH3)4 |
0.510 |
739 |
3.22 |