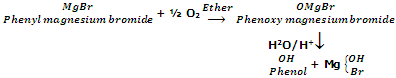The methods used for the preparation of phenols are given below:
From aryl sulphonic acids
Aryl sulphonic acids on fusion with NaOH at 573 K followed by acidification yield phenols.
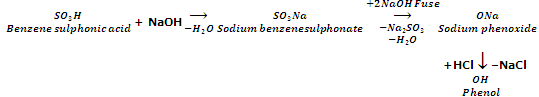
From aryl halides (Dow's process)
Phenol is obtained on a large scale by heating chlorobenzene with 10% NaOH solution at about 623 K and under a pressure of 300 atmospheres in the presence of copper catalyst.
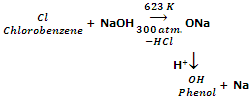
From diazonium salts
In the laboratory phenols are prepared hydrolysis of diazonium salts with water or dilute acids.
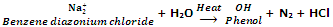
By decarboxylation of sodium salt of saclicyclic acid
Phenol can also be obtained by the decarboxylation of sodium salicyclate with soda lime (an equimolar mixture of NaOH and CaO).
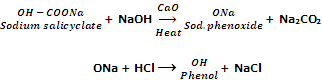
From Grignard's reagent
when oxygen is bubbled through the solution of phenylmagnesium bromide in ether, it forms an addition product which on acidification with dilute acid gives phenol.