During the formation of polymers, different macromolecules have different degree of polymerisation i.e. they have varied chain lengths. Thus, the molecular masses of the individual macromolecules in a particular sample of the polymer are different. Hence, an average value of the molecular mass is taken. There are two kinds of average molecular masses of polymers.
1. Number-average molecular mass 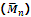
2. Mass-average molecular mass 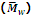
The two types of molecular masses are defined and calculated as follows:
1. Number-average molecular mass
When the total mass of all the molecules of a sample is divided by the total number of molecules, the result obtained is called the number-average molecular mass. For example, suppose in a particular sample
N1 molecules have molecular mass M1 each.
N2 molecules have molecular mass M2 each.
N3 molecules have molecular mass M3 each and so on. Then, we have
Total mass of all the N1 molecules = N1M1.
Total mass of all the N2 molecules = N2M2.
Total mass of all the N3 molecules = N3M3 and so on.
∴ Total mass of all the molecules = N1M1 + N2M2 + N3M3 + .....
= ΣNiMi
Total number of all the molecules = N1 + N2 + N3 + ....
= ΣNi
Hence the number-average molecular mass will be given by
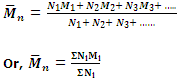
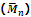 is generally determined by osmotic pressure measurement.
is generally determined by osmotic pressure measurement.
2. Mass-Average molecular mass
When the total mass of groups of molecules having different molecular masses are multiplied with their respective molecular masses, the products are added and the sum is divided by the total mass of all the molecules, the result obtained is called the mass-average molecular mass. Supposing, as before that N1, N2, N3, etc, molecules have molecular mass M1, M2, M3 etc. correspondingly.
Total mass of N1 molecules = N1M1.
Total mass of N2 molecules = N2M2.
Total mass of N3 molecules = N3M3 and so on.
The products with their respective molecular masses will be (N1M1 × M1), (N2M2 × M2), (N3M3 × M3), etc. i.e. N1M12, N2M22, N3M32, etc.
Sum of the products = N1M12 + N2M22 + N3M32 + ......
= ΣNiMi2
Hence the mass-average molecular mass is given by
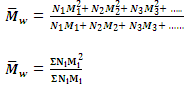
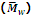 is generally determined by technique like ultra centrifugation of sedimentation.
is generally determined by technique like ultra centrifugation of sedimentation.