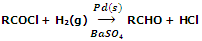Catalyst is a substance which accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any change in its chemical composition or mass during the reaction. The phenomenon of increasing the rate of a reaction with the help of a catalyst is known as catalysis.
For example, decomposition of potassium chlorate to give dioxygen occurs at high temperature in the range of 653 - 873 K
2KClO3  2KCl + 3O2
2KCl + 3O2
However, if a small amount of MnO2 is added to KClO3, its decomposition becomes faster and occurs at lower temperature range 473 - 633 K. the mass and chemical composition of MnO2 remains unaltered at the end of reaction. Thus, MnO2 acts as catalyst for the decomposition of KClO3.
Catalytic action
Since the catalysts are not consumed during the reaction, therefore, only a small amount of catalyst is sufficient to catalyse the reaction. According to modern views, a catalyst speeds up the reaction by providing an alternate path of lower activation energy to the reactants. The catalyst lowers the activation energy by interacting with the reactants leading to the formation of some intermediate complex of lower potential energy. In due course, the intermediate complex decomposes to give the products and also the catalyst.
Promotors and poisons
Promotors are the substances which enhance the activity of catalysts. For example, in the Hber's process for the manufacture of ammonia, molybdenum (Mo) is used as promoter which increases the activity of iron (Fe) used as catalyst
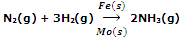
Poisons are the substances which decrease the activity of catalyst. For example, during the Rosemnud's reaction involving the hydrogenation of acetyl chloride, Pd is used as catalyst while BaSO4/quinoline acts as poison. This activity of catalyst is purposely decreased to check the reduction of RCOCl to RCHO stage. If this is not done the desired compound RCHO will further undergo reduction to form alcohol RCH2OH.