Straddle & Strangle: In the case of shorting butterfly spread, it can be seen that the gains are limited. However, there exists another strategy known as straddle which produces unlimited gains. This strategy benefits when the trader expects that there would be significant volatility in the market movements. In straddle, the investor buys both the calls and the puts that have the same exercise price and are on the same underlying and have the same time to expiration.
The initial outflow would be high as the premium of both the call options and the put option would have to be paid which implies a total outflow of c + p. In this strategy, the investor profits from both the upside and downside moves. The value of the strategy at expiration is given by:
Value = max (0, ST – X) + max (0, X – ST)
The value accrues on account of the gains that are realized by either in the call option or the put option. Note that if one option pays off, the other option exercises worthless as the price movement can be in one direction only. As there is an initial outflow of c + p, the net profit that results from the strategy is given by the equation:
Profit = max (0, ST – X) + max (0, X – ST) – c – p.
The payoff diagram along with the values and profits in different scenarios has been represented in the following graph:
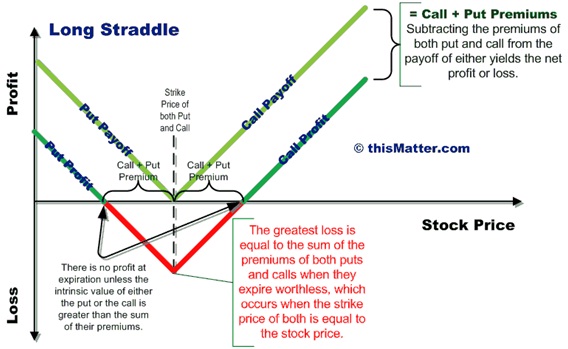
As can be seen from the graph, the gains are unlimited in this strategy while the losses are limited and the maximum loss is limited to the initial premium outflow represented by c + p. However, for the straddle to yield profits, it is essential that the movement in the prices of the underlying is high so that the option premiums of both call and put can be compensated for. If the movements are low, the payoff would be nullified by the high option premium paid at the upfront.
This strategy is used by investors who expect the markets to be highly volatile but are uncertain about the direction of movement. If the trader has an expectation about the market movement, he/she may add a call/put to a straddle strategy and this is respectively known as strap and strip. Another type of strategy is strangle in which the put and the call options have different exercise prices. The payoff would be similar to the straddle, but the pointed section at the bottom (representing the losses) would be flat since the losses would be in range on account of the differing exercise prices.