Carbon compounds containing more than one halogen atom are called polyhalogen compounds. Most of these compounds are valuable in industry and agriculture. Some important polyhalogen compounds are described as follows:
Dichloromethane or methylene chloride, CH3Cl2
Dichloromethane is prepared industrially by direct chlorination of methane. The mixture of CH3Cl, CH2Cl2, CHCl2 and CCl4 so obtained is separated by fractional distillation.
Properties
Dichloromethane is a sweet smelling volatile liquid and its boiling point is 313 K.
Dichloromethane harms the human central nervous system. Exposure to lower levels of dichloromethane in air can lead to slightly impaired hearing and vision. Higher levels of dichloromethane in air can cause dizziness, nauses and numbness in the fingers and toes. Direct skin contact with methylene chloride causes strong burning and mild redness to the skin. Direct contact with eyes can burn cornea.
Uses
Because of its low boiling point and low inflammability it is used as extraction solvent in pharmaceutical and food industries. It is also used as solvent for carrying out many organic reactions in research laboratories.
It is used as a metal finishing and cleaning solvent.
It is also used as a propellent in aerosols.
Trichloromethane (Chloroform), CHCl3
Preparation
From methane: chloroform is manufactured by chlorination of methane in the presence of light or catalysts.
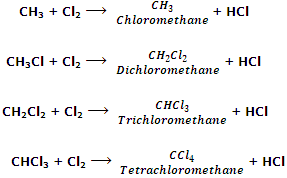
The mixture of CH3Cl, CH2Cl2, CHCl3 and CCl4 can be separated by fractional distillation.
From chloral hydrate, pure chloroform can be obtained by distilling chloral or chloral hydrate with concentrated aqueous solution or KOH solution.
NaOH + CCl3CHO 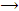 HCOONa + CHCl2
HCOONa + CHCl2
NaOH + CCl3CH(OH)2 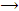 HCOOna + CHCl3 + H2O
HCOOna + CHCl3 + H2O
Laboratory method: in this method chloroform is obtained from ethanol or acetone by reaction with a paste of bleaching powder and water.
In this reaction, bleaching powder serves as a source of chlorine which first oxidizes ethanol acetaldehyte, which is then further chlorinated to chloral. Chloral reacts with Ca(OH)2, given by CaOCl2, to give chloroform and calcium formate.