The equilibrium constant can be treated as a particular type of molecular distribution. Consider the simplest gas-phase reaction, one in which molecules of A are converted to molecules of B. the reaction, described by the equation
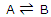
Will proceed until a state of equilibrium is reached. Then, at a given temperature, there will be some ratio of the number of B molecules to the number of A molecules. Now we investigate what it is about the A and B molecules that determine the ratio of the numbers present in equilibrium. This simple, artificial example will show what molecular level factors operate to determine the position of a chemical equilibrium.
Consider the generalized patterns of energies of the states of the chemical species A and B in their standard states. The difference in the energies of the A and B states of lowest energy is εB0- εA0 = Δε0. This quantity is familiar as the molar quantity UB0 - UA0 = ΔU0, the difference in energy between 1 mol of A and 1 mol of B if all the molecules of both species are in their lowest possible energy states.
On a molecular basis, the question of the position of the equilibrium between A and B is phrased in this way. If a large number of molecules are allowed to equilibrate and distribute themselves throughout the energy level pattern of many as B molecules, i.e. occupy the B levels? The question is answered by application of the Boltzmann distribution expression.
Let NA0 be the number of molecules, which, at equilibrium, occupy the lowest energy level. This happens to be an A level. The total number of molecules in the A levels, indicated by Nam is given, according as
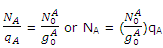
In a similar way the number of molecules NB distributed throughout the B levels is related to the number in the lowest-energy B states by
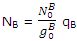
Since equilibrium is established between the distribution throughout the A and B states, the population of the lowest B state is related to the population of the lowest A state by the Boltzmann expression
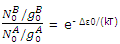
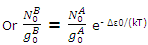
The expressions for the population of B levels can now be rewritten as
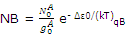
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of A to B might be expressed as the ration of the pressure or the concentration of B to A. both these terms will be dependent on, and proportional to, the number of moles or molecules of the two reagents. We can therefore write
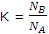
The expressions for NB and NA can now be substituted to give
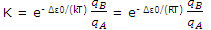
This result can be applied to any molecular transformation of the type 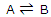 .
.
Notice that the formation of B is favored by ΔU0 values that are small or negative. This term is temperature independent (although it does enter the temperature dependent term = e- Δε0/(RT)and is not determined by the pattern of energy levels. The formation of B is also favored by a large value of qB relative to that qA. Large partition function value result, according to the discussion, when many states are available to the molecules. Thus, the formation of B will be favored if the energy of the states of B are closely spaced and the number of states corresponding to these allowed energies is high.
The very simple example can be used to illustrate these general conclusions. The partition functions are very simply calculated as
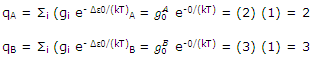
The equilibrium constant for the system can be calculated at the two temperatures of, say, 25and 1000°C. Equation can be used to give
K298 = e-1200/(8.314) (298) (3/2) = 0.92
K1273 = e-1200/(8.314) (1273) (3/2) = 1.34