The arc elasticity of Plastibristle’s demand for labor in between point c and point d is approximately: (1) 0.375. (3) 0.545. (4) 0.833. (4) 1.200 (5) 2.000.
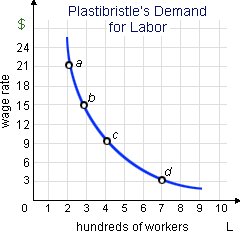
I need a good answer on the topic of Economics problems. Please give me your suggestion for the same by using above options.