Carlos and Ivana are friends and roommates. They eat together despite who cooks. But this cooking game is repeated mostly every evening, across time the probable result would be which: (1) neither Carlos nor Ivana cook, nor do they eat. (2) Carlos alone cooks for both of them every night. (3) Ivana alone cooks for both of them nightly. (4) Carlos and Ivana share the cooking chores every night, and after that they eat together. (5) some nights Carlos cooks alone, some nights Ivana cooks alone, and a few nights, they share the cooking chores.
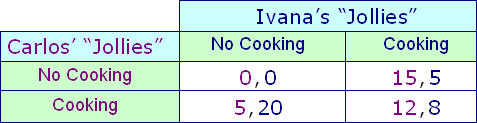
Please choose the right answer from above...I want your suggestion for the same.