The electric charge acquired by macromolecules affects the equilibrium set up across a semipermeable membrane.
Laboratory studies of macromolecule solutions as in osmotic pressure and dialysis studies confine the macromolecules to one compartment while allowing passage of small ions or solvent in or out compartment. Much of the transport occurring in cells and cell compartments in living systems can be similarly described. In all such cases, the equilibrium state that would be reached as a result of the net transport of the small ions can be markedly affected if the macromolecule carries a charge, as is generally the case.
Except at the isoionic pH, proteins and nucleic acids carry a charge as a result of a net gain or loss of protons. Additional charges are acquired by the binding of other species, e.g. the binding of Mg2+ ions by phosphate groups. Thus, macromolecules in laboratory or biological systems generally carry a charge. The overall electrical neutrality of the solution results from a corresponding opposite charge contributed by ions, called counterions, included in the remaining ionic make up of the solution.
Suppose such a macromolecule or, specifically, a protein solution is separated from pure water by a semipermeable membrane that allows passage of small ions but prohibits the passage of protein molecules. Such a situation could arise in an osmotic pressure study or in the dialysis of the protein solution. Suppose the protein carries a net negative charge and that Na+ ions are the counterions. The Na+ ions will tend to diffuse to the low concentration region of initially pure water. Electrical neutrality would be lost and this process prevented if it were not for the dissociation of water. This occurs, and H+ ions tend to accumulate on the proteins side of the membrane while the corresponding OH- ions accumulate, along with the buffered, pH charges will occur to upper the osmotic pressure or dialysis experiment.
In such ways are led to deal with the equilibrium between protein solutions, which are often themselves buffered, and buffer solutions. The complication arise can be illustrated by considering the simplest situation of the protein-sodium-ion solution separated by a semipermeable membrane from a sodium chloride solution.
Suppose the proteins species P carries a negative charge of -z. the neutrality of the solution is achieved by the presence of z positive charges, Na+ ions for example, for each protein concentration is cP, as the initial Na+ concentration in the protein compartment is zeP.
Species concentration in a Donnan-membrane equilibrium study:
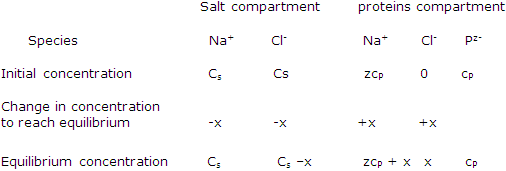
Rearrangement leads to x, the concentration of chloride that develops in the protein compartment:
At large salt concentrations, the effect of the protein is overwhelmed and x = 1/2cs. The two compartments achieve equal salt concentrations. At large a protein concentration, however, the passage of salt into the protein compartment is prevented, even though this rejection of the chloride ion by a solution that contains none of that ion.
Donnan-membrane equilibrium calculated from the above equation for z = 1:
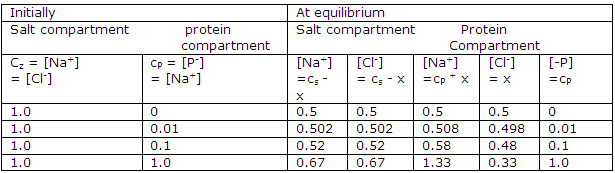
The effects of various concentrations of protein and electrolyte are shown in the table. Only at high concentration relative to the protein concentration is the effect of the confined charged protein small. Therefore many studies of proteins or other polyelectrolytes in solution are made at high electrolyte concentration and at a pH near the isoionic point.