Hypothetical production possibilities tables for New Zealand and Spain are given below
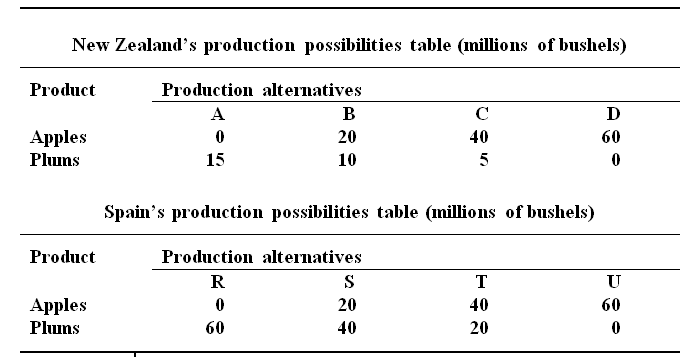
Employing a graph, draw the production possibilities data for each of the two countries. Referring to graphs, Find out:
(a) Each country's domestic opportunity cost of generating plums and apples.
(b) Which nation has to specialize in which product.
(c) The trading possibilities lines for each of the nation if the real terms of trade are 1 plum for 2 apples.
(d) Profit after trade.