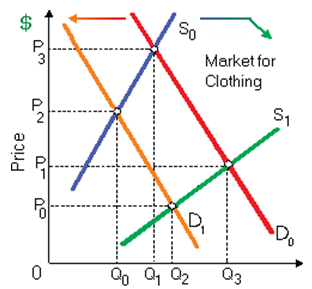
This vigorously competitive clothing market is at firstly in equilibrium at S0 and D0. When the moves in the demand for clothing to D1 occurred before the transfer in supply to S1, in that case: (1) the primary signal to firms that some disruption had arisen would be unexpected declines within inventories, manifested like shortages. (2) after first shortages of clothing, surpluses would finally drive the price up from P1 towards P3. (3) inventories would develop unexpectedly, with continuous surplus clothing while the price fell from P3 till this settled at P0. (4) clothing firms would experience increasing profits at first, and in that case declines back to an equilibrium rate of profit. (5) a new clothing fad possibly accounts for the change within demand, when increasing textile prices may account for the downward transfer in supply.