1. Physical state: the first three aliphatic acids are colourless liquids with pungent smell. The next six are oily liquids with an odour of rancid butter while the higher members are colourless, odourless waxy solids. Benzoic acid is referred to as crystalline solid.
2. Solubility the first four aliphatic members are soluble in water due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water molecules.
With increasing size of alkyl groups, the non-polar part of the molecule predominates thereby reducing the solubility in water. The higher members are almost insoluble in water.
3. Boiling points: carboxylic acids have quite high boiling points due to presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding which results in the formation of dimeric structures.
Due to dimeric structure, the effective molecular mass of the acid becomes double the actual mass. Hence, carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Moreover, O-H bond in carboxylic acids is more polar than O-H bond in alcohols. This is due to electron withdrawing effect of carbonyl group on O-H. Hence, H-bonds in carboxylic acids are comparatively stronger than those of that in alcohols.
4. Melting points: in first ten members of homologous series, the alternation effect is observed. The alternation effect implies that the melting point of an acid with even number of carbon atom is higher than the acid with odd number of carbon atoms above and below it. However, no such effect is observed in homologues with more than ten carbons. The alternation effect can be explained on the basis of the fact that the carboxylic acids with even number of carbon atoms, the terminal methyl group and carboxyl group of the opposite sides of zig-zag carbon chain. Hence, they fit better in the crystal lattice and it results in stronger intermolecular forces. On the other hand, acids with odd number of C atoms have carboxyl and terminal methyl number of C atoms has carboxyl and terminal methyl groups on the same side of zig-zag carbon chain. Therefore, such molecules being relatively unsymmetrical, fit poorly in the crystal lattice. This causes weaker intermolecular forces and accounts for the relatively lower melting points.
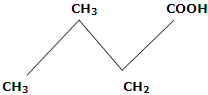
Even number of C-atoms, fit better, in crystal lattice, have higher m.pts (Terminal groups are on opposite side)
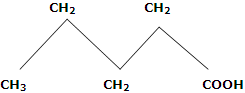
Odd numbers of C-atoms, fit properly, in crystal lattice, have lower m.pts. (Terminal groups are on same side).
The melting and boiling points of aromatic acids are generally higher than those of aliphatic acids of similar molecular masses. This is presumably due to the fact that planar benzene ring in these acids can pack closely in the crystal lattice than zig-zag aliphatic acids.