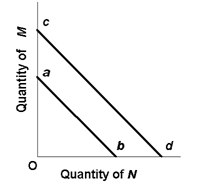
The shift of the budget line from cd to ab in the below given figure is consistent with: 1) decreases in the prices of both M and N . 2) an increase in the price of M and a decrease in the price of N . 3) a decrease in money income. 4) an increase in money income.
Can some one help me in above que?