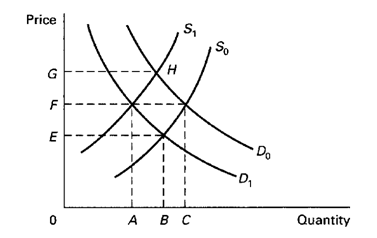
Refer to the following diagram, which depictes demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. A shift in the demand curve from D0 to D1 might be caused by a(n): 1) decrease in income if X is an inferior good. 2) increase in the price of complementary good Y. 3) increase in money incomes if X is a normal good. 4) increase in the price of substitute product Y.
Help me to get through this problem