Wffs (Well-formed formulas): These are defined inductively by the following clauses:
(i) If P is an n-ary predicate and t1, …, tn are terms, then P(t1, …, tn) is a wff. (Such a wff is atomic.)
(ii) If α is wff, then ¬ α is a wff.
(iii) If α and β are wffs, then α → β is a wff.
(iv) If α is a wff and x is an individual variable then
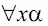
is a wff.
The connectives are operators, which act on wffs, yielding other wffs; ¬ is a unary operator (it acts on a single wff), → is a binary operator. Also a quantifier, coupled with a variable, is a unary operator that acts on wffs. We require that any wff that is thus generated has a unique decomposition into components. The notation should be such as to yield a unique readability theorem.