The information is illustrated below:
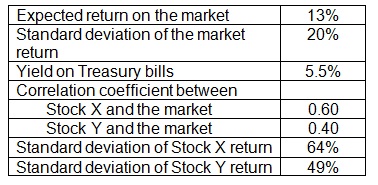
(a) Determine the expected return on Stock X?
(b) Evaluate the expected return on Stock Y?
(c) Assume that you have $5,000 to invest in a portfolio made up of Stocks X and Y. How will you allot your funds between Stock X and Stock Y in order to attain a portfolio return of 15.67 percent?
(d) Compute the beta of the portfolio in part (c). How risky is this portfolio? Describe.
(e) Your friend recommends that you purchase Stock Z which has a beta of 2.76 and has an expected return of 21.75 percent. Would you purchase Stock Z? Describe.