Question:
Ambrose consumes two goods, peanuts (x1 ) and a composite good (x2). He has a utility functionU = 4 √x1 + x2. This means his MU1 = 2/ √x1 and his MU2 = 1 . The current prices are p1 = 0.5 per kilogram and. p2 = 1. His budget is $20 per month.
(a) Write down Ambrose's budget constraint?
(b) What are the optimal quantities of peanuts and x2 for Ambrose to consume? How much utility will he get?
(c) Suppose that rationing by the government means that Ambrose is allowed to purchase no more that 12 kilograms of peanuts per month. Now how much x1 and x2 will Morgan consume? Show the effect of rationing using a diagram. Be sure to label you diagram completely.
(d) Suppose that instead of rationing peanuts the government decides to tax them. The tax is $0.5 per kilogram. How much x1 and x2 will Morgan consume? How much utility will he get?
(e) How much would Ambrose need to be compensated to make him as well of as if peanuts had not been taxed?
Solution:
a) P1 = 0.5, P2 = 1, m = 20
Therefore, the budget constraint is,
0.5x1 + x2 = 20
b) U = 4 Öx1 + x2. P1 = 0.5, P2 = 1
MRS = MU1/ MU2 = (2/Öx1)/1 = 2/Öx1
Now, MRS = P1/P2 = 0.5/1 = 2/Öx1
- Öx1=2/0.5
- x1 = 4/0.25 = 16
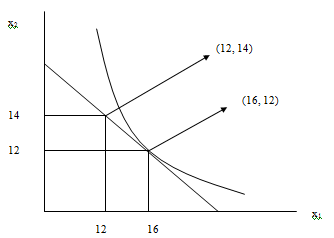
- x2 = (20 - 16x 0.5) = 12
Utility derived = 4(16)0.5 + 12 = 28
c) If x1 is rationed to 12 units, x2 = 20 - 12x 0.5 = 14
d) P1 = 0.5 + 0.5 = 1, P2 = 1, m = 20
MRS = P1/P2 = 1/1 = 2/Öx1
- Öx1=2
- x1 = 4
- x2 = (20 - 4x 0.5) = 18
Utility derived = 4(4)0.5 + 18 = 22
e) 4(4)0.5 + x2 = 28
- 4 + x2 = 28
- x2 = 28-4 = 24
- Extra money required = 24 - 18 = 6