Abstract:
Nowadays, in the age of internet, all has gone wireless. Now the world follows a new prototype from long cables to no cables. The technology of wireless mobile is growing in fast pace with advanced techniques. The progress in telecommunication has put ahead a huge step in the progression of mobile networks. The swift growth of the mobile generations was for the motive of sustaining loads of mobile devices as possible that could benefit the users anywhere and at anytime in terms of general realistic applications like internet access, video-on-demand, video conferencing, mobile entertainment services, mobile financial services and many more. Beginning from the scratch to today’s hottest approach, this presents a review for the mobile generations in the wireless communication field in order to highlight and compare the issues and confronts that are concerned in each and every generation.
Introduction:
In this research work, we try to explore the detail analysis of the different generations of the mobile networks. First Generation (1G) mobile phone networks were the most fundamental systems to build up and they totally rely on a network of distributed transceivers to communicate by means of the mobile phones. Second Generation (2G) mobile networks were the logical following stage in the growth of wireless systems after 1G, and at the very first time they introduced a mobile phone system which employed exclusively digital technology. Third Generation (3G) mobile networks are the up-to-date stage in the growth of wireless technology. The key features of 3G systems are that they support much higher data communication rates and proffer increased capability that makes them suitable for high-speed data applications and also for the conventional voice calls. Fourth Generation (4G) is beyond 3G, stands as an acronym for the Fourth-Generation Communications System. A 4G system will be capable to present a complete IP justification in which voice, data and streamed multimedia can be provided to users anywhere, anytime at finer data rates. Fifth Generation (5G) is a packet switched wireless mobile communication system by means of extensive area coverage and hence it is known as wireless World Wide Web.
Evolution of Mobile Cellular Networks:
The mobile communication has generations as illustrated in the figure. The brief explanation of every generation is as follows:
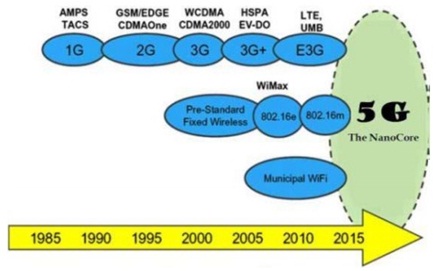
First Generation Technology:
1G signifies to the first generation of mobile communication system started in the year 1974 and finished in the year 1984. 1G was build up on earlier phases to communicate with the mobile phones via the network of distributed transceivers. Analog System was the initial mobile wireless communication system utilized in 1G, based on an AMPS technology, which was based on frequency modulation radio system employing FDM with 30 KHz as the channel capacity and frequency band was 824-894 MHz it permits only voice calls. The speed is up to 2.4 Kbps.
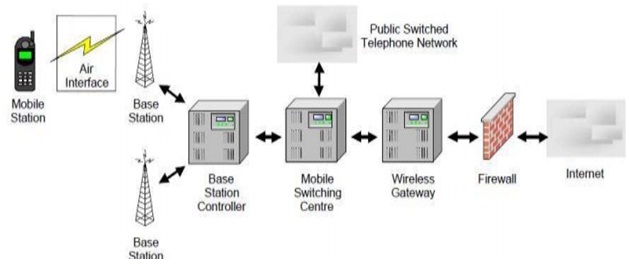
There are few limitations in the 1G communications.
- It consists of no data service that can modify the voice into digital numbers.
- The global roaming service was not presented.
- There was only one channel that carries the data from one caller (source) to the other (destination). This signifies that the two callers are not able to hear each other alongside.
Second Generation Technology:
2G is the short form for second-generation wireless telephone technology. In this, SMS messaging is offered as a form of data-transmission for some standards. 2G cellular telecom networks were commercially started on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja in the year 1991. GSM service is utilized by more than 2 billion people across over 212 countries and territories. The ubiquity of the GSM standard formulates international roaming exceptionally ordinary between mobile phone operators, allowing subscribers to make use of their phones in various parts of the world. 2G technologies can be categorized into TDMA based and CDMA based standards based on the kind of multiplexing employed. They mainly use CODEC to compress and multiplex digital voice data.
The benefits of 2G comprise less battery power, Digital coding enhances the clearness of the voice and decreases noise in the line and are considered environment friendly. The utilization of digital data service helps mobile network operators to take in short message service over the mobile phones. Digital encryption has offered security and privacy to the data and voice calls.
Third Generation Technology:
3G in mobile phones is the technology, intervening 2G, and preceding 4G. This is built on the ITU family of standards in the International Mobile Telecommunications program, IMT-2000.
3G technologies let network operators to provide users a broader range of more advanced services whereas achieving superior network capacity via improved spectral efficiency. Services include wide area wireless voice telephony, video calls and broad-band wireless data, all in a mobile atmosphere. Additional features as well comprise HSPA data transmission skills that are capable to deliver speeds up to 14.4Mbit/s on the downlink and 5.8Mbit/s on the uplink.
3G networks are mainly wide area cellular telephone networks which evolve to integrate high-speed internet access and video telephony. It makes use of TDMA and CDMA all along with value added services such mobile television, GPS and video conferencing. The fundamental mark of 3G technology is speedy data transfer rates. This technology is much flexible, as it is capable to support the 5 major radio technologies which work under CDMA, TDMA and FDMA.
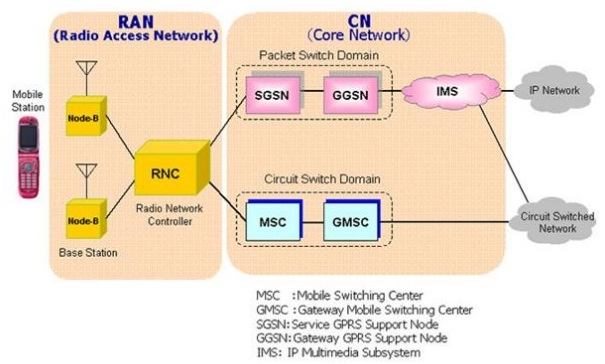
The main aim of the 3G is to allow for more coverage and expansion with minimum investment having following improvements over previous networks:
- Improved audio-video streaming
- Several times higher data speed
- Support of Video-conferencing
- Web and WAP browsing at higher speeds;
- IPTV support
Fourth Generation Technology:
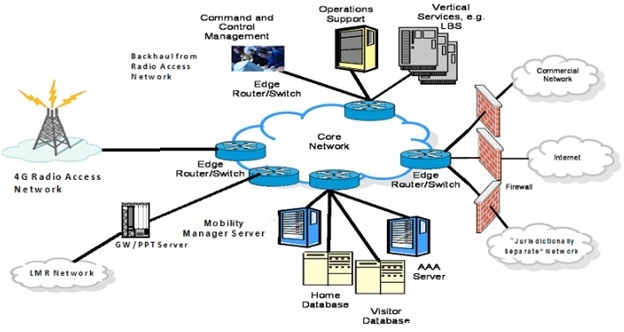
4G network is the name provided to an IP-based mobile system which gives access via a collection of radio interfaces. A 4G network makes sure flawless roaming and excellent connected service, merging many radio access interfaces to a single network that subscribers might use. By this feature, users will have access to various services, enhanced coverage, ease of a single device and more reliable wireless access even with the breakdown or loss of one or more networks.
At the most general level, 4G architecture will encompass three fundamental areas of connectivity: Personal Area Networking, local high-speed access points on the network all together with wireless LAN technologies and cellular connectivity.
To summarize, the roots of 4G networks lie in the proposal of pervasive computing. 4G is being build up to accommodate the QoS and rate requirements set by imminent applications such as wireless broadband access, MMS, mobile TV, video chat, HDTV content, Digital Video Broadcasting, minimal services such as voice and data, and other services which make use of bandwidth. The meaning of 4G is to offer adequate RF coverage, more bits/Hz and to inter-connect all wireless heterogonous networks to offer seamless, steady telecom familiarity to user.
Fifth Generation Technology:
The 5G wireless mobile communication system is the wireless internet network that is maintained by OFDM, MC-CDMA, LAS-CDMA, UWB, Network-LMDS and IPv6. The 5G is as well termed as Real world wireless or wwww worldwide wireless web as it doesn’t need restrictions.
Physical layer and data link layer states the wireless technology in 5G. Such two layers point out that the 5G technology is similar to OWA and the virtual multi-wireless networks are as well maintained in the 5G technology mobile phones. To do this, the network layer is sub categorized into upper network layer for upper terminal and lower network layer for interface and in which all the routing is based in IP addresses and that must be different for each and every IP network in global. The main disadvantage of the 5G technology is high big rate. The big rate is controlled by employing OTP. Such OTP is supported via transport layer and session layer in 5G networks. The application layer is for quality of service management over different kind of networks. Bidirectional bandwidths, less traffic, uniform accessibility of network across the world, 25Mbps connectivity speed, data bandwidth privileged than 1GB and low cost are the key characteristics of 5G technology.
Conclusion:
Mobile has churn out to be very vital component of our life. Their present growth is the result of different mobile generations. The fundamental trends and technology have been utilized in the past decade to enhance the performance by following the advantages and disadvantages of one generation over other. The advent of 5G will definitely modernize the field of communication domain; taking wireless experience to an absolutely new level. This technology assists to support stronger links among peoples working in different fields making future concepts of mobile communication, internet service and cloud computing.